Background
Allogeneic stem cell transplantation (alloSCT) is the cornerstone therapy for myelodysplastic syndromes with increased blasts-2 (MDS-IB2). However, the optimal induction therapy before transplantation remains unclear. Herein, we compared our single-center experience of non-intensive Venetoclax (Ven)-based regimens versus standard intensive chemotherapy (IC) as bridging to alloSCT in MDS-IB2 patients.
Methods
We have performed an observational, retrospective, single-center study. All patients were at least 18 years of age, had newly diagnosed, previously untreated MDS-IB2 based on the 5 th edition of the WHO diagnostic criteria, were considered transplant-eligible at diagnosis, and had received either Ven-based therapies or IC for induction. All patients provided informed consent for data collection. The Ven-based regimens were either Ven14+Aza7 (Venetoclax 400mg/d on days 1-14 with Azacitidine 75mg/m 2 on days 1-7) or ACTIVE (Venetoclax 600mg/d on days 1-14, Cytarabine 20mg/m 2 on days 1-10 and Actinomycin D 12.5mcg/kg on days 1-3). IC regimens were 7+3 or FLAG-Ida. After 1 or 2 cycles of induction therapy transplant-eligible responders proceeded to alloSCT. We evaluated baseline characteristics, IPSS-M, IPPS-R values, CR, CRh and marrow CR (mCR) rates, time to ANC>1x10 9 and PLT>100x10 9 recovery, CTCAE v5.0 grade 3-5 non-hematological adverse events, overall survival (OS) and day-30 mortality.
Results
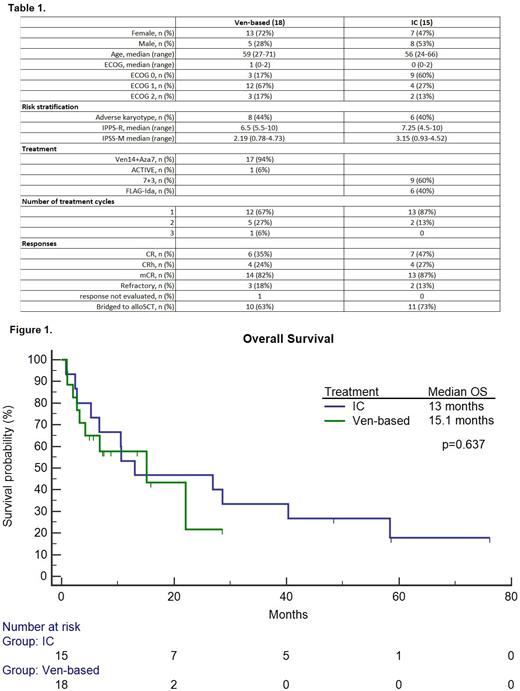
Detailed baseline characteristics are summarized in Table 1. 18 patients (13 female) had received Ven-based therapies and 15 patients (7 female) had undergone IC. The median age was 59 (27-71) in comparison to 56 (24-66) in Ven and IC patients, respectively (p=0.104). The median ECOG value was 1 (0-2) in the Ven group and was significantly higher compared to 0 (0-2) in the IC cohort (p=0.042). The median IPSS-R and IPSS-M values were 6.5 (5.5-10) and 2.19 (0.78-4.73) compared to 7.25 (4.5-10) and 3.15 (0.93-4.52) in Ven and IC patients, respectively (p=0.746, p=0.79). The mCR rate was 82% in Ven patients compared to 87% in the IC group (p=0.741). The CR+CRh rates were 59% and 73% in Ven and IC groups, respectively (p=0.396). Sixty-three percent of Ven patients were allotransplanted compared to 73% in the IC group (p=0.526). Grade 3-5 non-hematological toxicity was lower in the Ven group compared to the IC patients (44% vs 87%, p=0.013). The median times to neutrophil and platelet recovery were 44 (4-165) and 34 (21-94) days compared to 30 (21-110) and 32 (21-36) days in the Ven and IC groups, respectively (p=0.285, p=0.775). The median OS was 15.1 months (3.2-22.1) and 13 months (6.7-40.3) in the Ven and IC groups, respectively (p=0.637). Survival data are shown in Figure 1. The day-30 mortality rate was 11% in the Ven group compared to 7% in the IC patients (p=0.663).
Conclusions
We did not observe significant differences between low-intensity Ven-based regimens and IC in terms of responses, overall survival, and number of transplanted patients in this high-risk MDS-IB2 cohort. Non-hematological grade 3-5 toxicity was lower in Ven-treated patients. Our real-life, single-center results should be interpreted with caution.
OffLabel Disclosure:
Zucenka:Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel Expenses; Astellas: Consultancy, Honoraria; Pfizer: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel Expenses; Jannsen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel Expenses; Takeda: Other: Travel expenses. Davainienė:Abbvie: Other: Travel Expenses. Čepulytė:Abbvie: Other: Travel Expenses. Davainis:Abbvie: Other: Travel Expenses. Pileckytė:Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel Expenses. Trociukas:Takeda: Other: Travel expenses. Griškevičius:Miltenyi Biomedicine: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Venetoclax: MDS-IB2

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal